| [1] Jemal A,Murray T,Samuels A,et al.Cancer statisticsl CA Cancer. Clin.2003;53(1):5-26. [2] Qiu WL,Zhang ZK,Zhang ZY,et al. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 2008: 164-166.邱蔚六,张震康,张志愿,等.口腔颌面外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008: 164-166.[3] Rechka A, Neagoe PE, Gratton JP ,et al.Identification of VEGF receptor-2 tyrosine phosphorylation sites involved in VEGF-mediated endothelial platelet-activating factor synthesis.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;88(10):968-976. [4] Kusumanto YH, van Weel V, Mulder NH,et al. Treatment with intramuscular vascular endothelial growth factor gene compared with placebo for patients with diabetes mellitus and critical limb ischemia: a double-blind randomized trial.Hum Gene Ther. 2006;17(6):683-691. [5] Ferrara N. Pathways mediating VEGF-independent tumor angiogenesis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.2010;21(1):21-26. [6] Bao P, Kodra A, Tomic-Canic M, et al. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Wound Healing. J Surg Res. 2009;153(2):347-358. [7] Carev D, Saraga M, Saraga-Babic M. Involvement of FGF and BMP family proteins and VEGF in early human kidney development.Histol Histopathol. 2008;23(7):853-862. [8] Lavu M, Gundewar S, Lefer DJ.Gene therapy for ischemic heart disease.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(5):742-750. [9] Arima K, Katsuda Y, Takeshita Y,et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells improved ischemic peripheral neuropathy in humans.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(3):238-239.[10] Emerich DF, Silva E, Ali O, Mooney D,et al. Injectable VEGF hydrogels produce near complete neurological and anatomical protection following cerebral ischemia in rats. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(9):1063-1071. [11] Liu H, Li XQ,Chen WP, et al.Xiandai Yiyuan.2009;9(1): 17-20. 柳晖,李新强,陈吴鹏,等.VEGF转染VEC促进移植皮瓣血管化的实验研究[J].现代医院,2009,9(1):17-20.[12] Avraham T, Daluvoy S, Zampell J, et al. Blockade of transforming growth factor-beta1 accelerates lymphatic regeneration during wound repair. Am J Pathol. 2010; 177(6): 3202–3214. [13] Liao CT,Chang JT,Wang HM,et al. Does adjuvant radiation therapy improve outcomes in pT1-3N0 oral cavity cancer with tumor-free margins and perineural invasion? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71(2):371-376. [14] Louise Kent M, Brennan MT, Noll JL,et al. Radiation-induced trismus in head and neck cancer patients.Support Care Cancer. 2008;16(3):305-309.[15] Li ZM,Qu XM,Xu SP,et al.Xiandai Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2009; 23(5):532-535.李志民,曲兴民,徐寿平,等.电离辐射对于大鼠咬肌细胞超微结构及糖原含量的影响[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2009,23(5):532-535.[16] Okunieff P,Wang X,Rubin P,et al.Radiation induced changes in bone perfusion and angiogenesis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.1998;42(4):884-889.[17] Martin M, Lefaix J, Delanian S.TGF-beta1 and radiation fibrosis: a master switch and a specific therapeutic target? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47(2):277-290.[18] Branski RC, Barbieri SS, Weksler BB,et al. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 on human vocal fold fibroblasts.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009;118(3):218-226. [19] Clavin NW, Avraham T, Fernandez J, et al.TGF-β1 is a negative regulator of lymphatic regeneration during wound repair. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;295(5):H2113-2127. [20] Kondo T,Ohshima T.The Dynamics of inflammatory cytokines in the healing process of mouse skin wound :a preliminary study for possible wound age determ ination.Int J Legal Med. 1996;108(5):231-236.[21] Xie JL.Guowai Yixue: Chuangshang yu Waike Wenti Fence. 1999;20(2):76-79.谢举林.转化生长因子-β在创伤愈合过程中的进展[J].国外医学: 创伤与外科问题分册,1999,20(2):76-79.[22] Liu H,Xiong M,Rong TH,etal.Aizheng.2008;27(1):18-24.刘慧,熊迈,戎铁华,等.大鼠心脏组织TGF-β1表达水平与放射性损伤关系的实验研究[J].癌症,2008,27(1):18-24.[23] Nomi M, Atala A, Coppi PD,etal.Principals of neovascularization for tissue engineering.Mol Aspects Med. 2002;23(6):463-483.[24] Gaengel K, Genové G, Armulik A, et al. Endothelial-mural cell signaling in vascular development and angiogenesis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(5):630-638. [25] Dickson MC, Martin JS, Cousins FM, et al. Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-β1 knock out mice. Development. 1995;121(16): 1845-1854. [26] Pepper MS. Transforming growth factor-beta: Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and vessel wall integrity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997;8(1):21-43. [27] Liu Y, Kudo K, Abe Y, et al. Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta, hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor reduced late rectal injury induced by irradiation. J Radiat Res. 2009;50(3):233-239.[28] Shen ZZ,Zheng JJ,Jia MY,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(15):2842-2845. 沈宗泽,郑建金,贾暮云,等. 放射性咀嚼肌损伤模型软组织病理改变及转化生长因子β1的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(15):2842-2845.[29] Frank S, Hubner G, Breier G, et al.Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes-Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem.1995; 270(21): 12607-12613.[30] Ferrari G, Cook BD, Terushkin V, et al. Transforming growth factor-1 (TGF-β1) induces angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2009; 219(2): 449-458. [31] Xia P,Tong WX,Yu YM,etal.Chongqing Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2010;35(8):1167-1171.夏鹏,童文祥,喻永敏,等.大鼠皮肤切创愈合过程中VEGF、TGF-β1蛋白的表达[J].重庆医科大学学报,2010,35(8): 1167-1171.[32] Berse B, Brown LF, Van de Water L, et al.Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor)gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages,and tumors. Mol Biol Cell. 1992;3(2):211-220.[33] Rocha FG, Sundback CA, Krebs NJ, et al. The effect of sustained delivery vascular endothelial growth factor on angiogenesis in tissue-engineered intestine.Biomaterials. 2008;29(19):2884-2890.[34] Grünewald FS, Prota AE, Giese A, et al. Structure–function analysis of VEGF receptor activation and the role of coreceptors in angiogenic signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804(3):567-580.[35] Ferrara N, Houck K, Jakeman L, et al. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992;13(1):18-32.[36] Taub PJ, Marmur JD, Zhang WX, et al. Locally administered vascular endothelial growth factor cDNA increases survival of ischemic experimental skin flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 102(6):2033-2039.[37] Romano Di Peppe S, Mangoni A, Zambruno G, et al. Adenovirus-mediated VEGF165 gene transfer enhances wound healing by promoting angiogenesis in CD1 diabetic mice. Gene Ther. 2002;9(19):1271-1277. [38] Zacchigna S,Tasciotti E,Kusmic C,et al. In vivo imaging shows abnormal function of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced vasculature. Hum Gene Ther.2007;18(6): 515-524. [39] Losordo DW, Vale PR, Hendel RC, et al. Phase 1/2 placebo controlled, double blind, dose-escalating trial of myocardial vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer by catheter delivery in patients with chronic myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 2002;105(17):2012-2018.[40] Muona K, Mäkinen K, Hedman M,et al. 10-year safety follow-up in patients with local VEGF gene transfer to ischemic lower limb. Gene Ther. 2012;19(4):392-395. [41] Enestvedt CK,Hosack L,Winn SR,et al. VEGF Gene Therapy Augments Localized Angiogenesis and Promotes Anastomotic Wound Healing: A Pilot Study in a Clinically Relevant Animal Model. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12(10): 1762-1770. [42] Vera Janavel GL, De Lorenzi A, Cortés C,et al. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer on infarct size, left ventricular function and myocardial perfusion in sheep after 2 months of coronary artery occlusion. J Gene Med. 2012;14(4):279-287. [43] Zhao N,Cheng Y,Liu YF,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(18):3571-3574.赵宁,程颖,刘永锋,等.真核表达载体血管内皮生长因子转染血管内皮细胞及对新生血管生成的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(18):3571-3574.[44] Huo WY,Yan X,Hao LY,et al.Zhonghua Laonian Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2010;8(2):102-106.霍文艳,颜兴,郝龙英,等.血管内皮生长因子对小型猪腮腺放射性损伤影响的实验研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2010,8(2): 102-106.[45] Wang DY,Yu DH,Wen YM,et al.Guangxi Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2005;22(3):326-328.王代友,于大海,温玉明,等.血管内皮生长因子基因转染对放疗后组织血管生成的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2005,22(3): 326-328.[46] Heikura T, Nieminen T, Roschier MM,et al. Baculovirus-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor-D gene transfer induces angiogenesis in rabbit skeletal muscle. J Gene Med. 2012;14(1):35-43.[47] Vasir B, Jonas JC, Steil GM,et al.Gene expression of VEGF and its receptors Flk-1/KDR and Flt-1 in cultured and transplanted rat islets.Transplantation. 2001;71(7):924-935. |
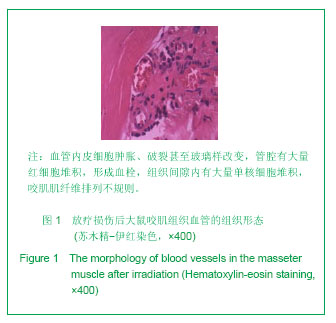
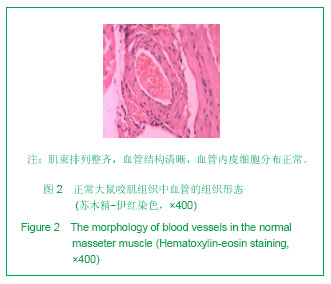
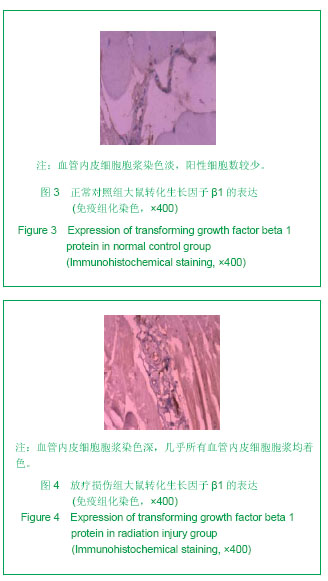

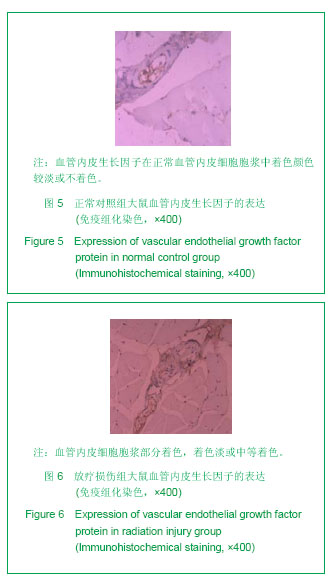
.jpg)